| Command |
Used where |
Function |
| pinMode(pin,IN/OUT) |
setup |
This defines which pins will be used and whether they ar inputs or outputs(TURNS OUT YOU ONLY NEED THIS FOR DIGITAL PINS) |
| digitalRead(pin) |
loop |
This will return a 1 or 0 depending on if the pin is high or low |
| digitalWrite(pin,HIGH/LOW) |
loop |
Will turn an output pin high or low depening on what you choose |
| delay(T) |
loop |
Creates a software delay(not accurate) of length T mili-seconds |
| If(1==1){code here} |
Both |
An if statement will run lines of code within the curly braces below it if the question in the circular brackets is true(check the bottom of the page for more info) |
| else{code here } |
Both |
If an if statement fails then it can run another section of code this is donated by else and curly braces |
| for(int a=0;a<=10;a++){code here} |
Both |
A for loop runs a section of code as many times as you tell it to in this case it will run for values a=0 to a=9 |
| Serial.print(showThisValue) |
loop |
When you want your arduino to interface with the computer you can send it information using this and read it in the serial monitor |
| Serial.begin(9600) |
setup |
This sets the Bode rate with the computer (communication frequency) and you can get gibberish back if you don't specify to the computer |
| analogRead(pin) |
loop |
Now this is for the analog pins compared to digital and will send back a value anywhere between 0 and 1023 (0 being low and 1023 being high) |
| analogWrite(pin,value) |
loop |
This now outputs a voltage from your set pin ranging from 0 to 255. Analogue write are actually PWM meaning actually just fast switching digital and therefore are from digital pins (ones that have PWM are denoted with a ~) |
| While(1==1){code here} |
both |
This will run a loop that will run until the case at the top is broken or it encounters break; |
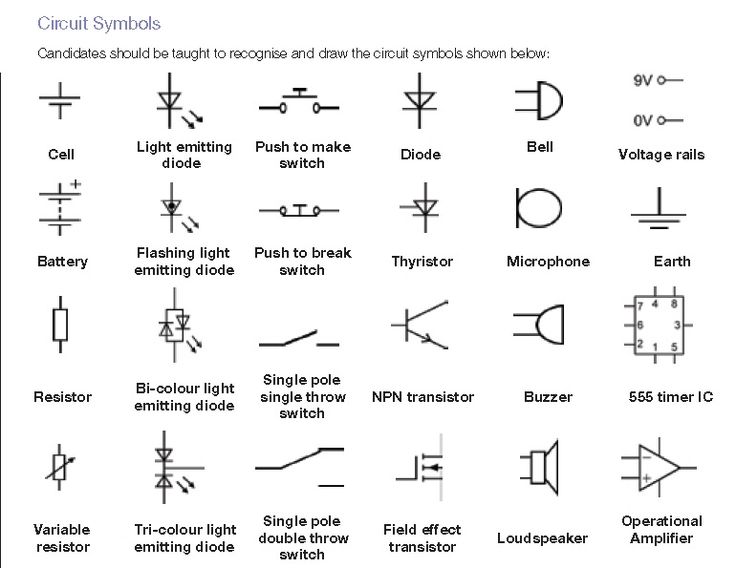 These are some of the most common componets you will come across, you should start getting used to them. If there is a component you don't know how to use just ask rather than popping them.
These are some of the most common componets you will come across, you should start getting used to them. If there is a component you don't know how to use just ask rather than popping them.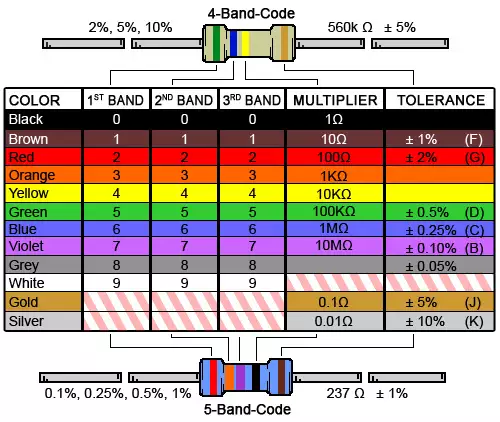 This is what all the funny colours on your resistors mean, read this by holding the brown/gold/silver band to the right and read off the values with the first ones meaning the actual numbers and then the last (excluding the gold/silver/brown) is your multiplier aka 2 would mean *100. The last band is the tolerance which is generally gold (+/-10% of the merked value) unless the resistance value is key
This is what all the funny colours on your resistors mean, read this by holding the brown/gold/silver band to the right and read off the values with the first ones meaning the actual numbers and then the last (excluding the gold/silver/brown) is your multiplier aka 2 would mean *100. The last band is the tolerance which is generally gold (+/-10% of the merked value) unless the resistance value is key